Family and social relationships address the child’s interactions with family members and their peers, and their ability to form and maintain healthy relationships. Social presentation and self-care needs address the child’s ability to present themselves appropriately in social situations and to take care of their own physical needs.
The court will often weigh these areas against what’s in the child’s best interest. Learn how that principle shapes decisions in our guide to the child’s best interest in family court.
Unsure how your child’s developmental needs might be judged? Tap WhatsApp and we’ll walk you through what really matters in court.
Parenting Capacity
Parenting capacity refers to a parent’s ability to meet the basic needs of their child, including ensuring safety, providing emotional warmth, stimulating their development, offering guidance and boundaries, and providing stability.
- Basic needs include things like food, shelter, clothing, and medical care. These are the most fundamental needs that must be met in order for a child to survive and thrive.
- Safety needs include things like protection from abuse and neglect, as well as a stable and secure environment. This includes emotional safety, physical safety, and safety from exploitation.
- Developmental needs include things like education, socialisation, and opportunities for growth and self-expression. These needs are important for the child’s overall development and well-being, including emotional, social, and cognitive development.
Ensuring safety involves providing a safe and secure environment for the child, protecting them from physical and emotional harm, and monitoring their well-being. Providing emotional warmth involves showing love and affection, being responsive to the child’s needs, and building a strong emotional bond with the child.
Stimulation involves encouraging the child’s intellectual, emotional, and physical development through activities, play, and learning experiences. Guidance and boundaries involve setting clear rules and expectations for the child’s behaviour and helping them to understand the consequences of their actions.
Stability refers to providing a consistent and predictable environment for the child, including a stable home, consistent routine, and a sense of security. It’s important to note that parenting capacity can be affected by a variety of factors, including a parent’s own emotional well-being, their life experiences and cultural background, and their knowledge of child development.
If you’re facing accusations that could undermine your parenting, it’s essential to understand what evidence the court actually considers when evaluating claims about parenting capacity.
Also, parenting is a continuous learning process that requires the parent to continuously assess and adapt their approach based on the child’s developmental stage, individual needs, and family dynamics.
Facing questions about your parenting capacity? Message us on WhatsApp today and get expert support to present your strongest case.
Family and Environmental Factors
Family and environmental factors are important considerations when assessing a child’s developmental needs. These factors can include family history and functioning, wider family dynamics, housing, employment, income, and family and social integration.
Family history and functioning can include a history of abuse or neglect, mental health issues, substance abuse, and other factors that may have an impact on the child’s development. Wider family dynamics can include the child’s relationships with grandparents, aunts, uncles, and other extended family members, and how these relationships may impact the child’s development.
Housing, employment, and income can also have an impact on a child’s development. For example, living in overcrowded or unsafe housing can have a negative impact on the child’s physical and emotional well-being, while stable employment and a sufficient income can provide a sense of security and stability for the family.
Finally, family and social integration and community resources can also play a role in a child’s development. This includes the child’s relationships with their peers, the availability of extracurricular activities and community resources, and the level of support provided by the community. It’s important to note that family and environmental factors can have both positive and negative impacts on a child’s development, and that addressing any negative factors can help to improve the child’s overall well-being.
Concerns around home life and external risk factors are often explored in fact-finding hearings. These hearings may examine whether allegations about your environment hold any weight in court.
Worried about how your home life will be judged in court? Tap WhatsApp and get tailored advice for your situation.
Final Thoughts
It’s important to note that these areas of development are interrelated and that addressing needs in one area can have a positive impact on other areas. Additionally, it’s important to consider the child’s unique needs and strengths, and to involve the child and their family in the assessment process.
In assessing the needs of children and families, it is important to consider all three areas of the triangle of needs and to develop a plan of action that addresses each of these areas.
🧠 Insider Insight: Lach, our founder, is a qualified social worker who used to write Section 7 reports for CAFCASS — the very reports that influence court outcomes. Now he helps dads respond to them. Learn more about Lach’s background.
👉 Learn more about how we can support you or book a free consultation today
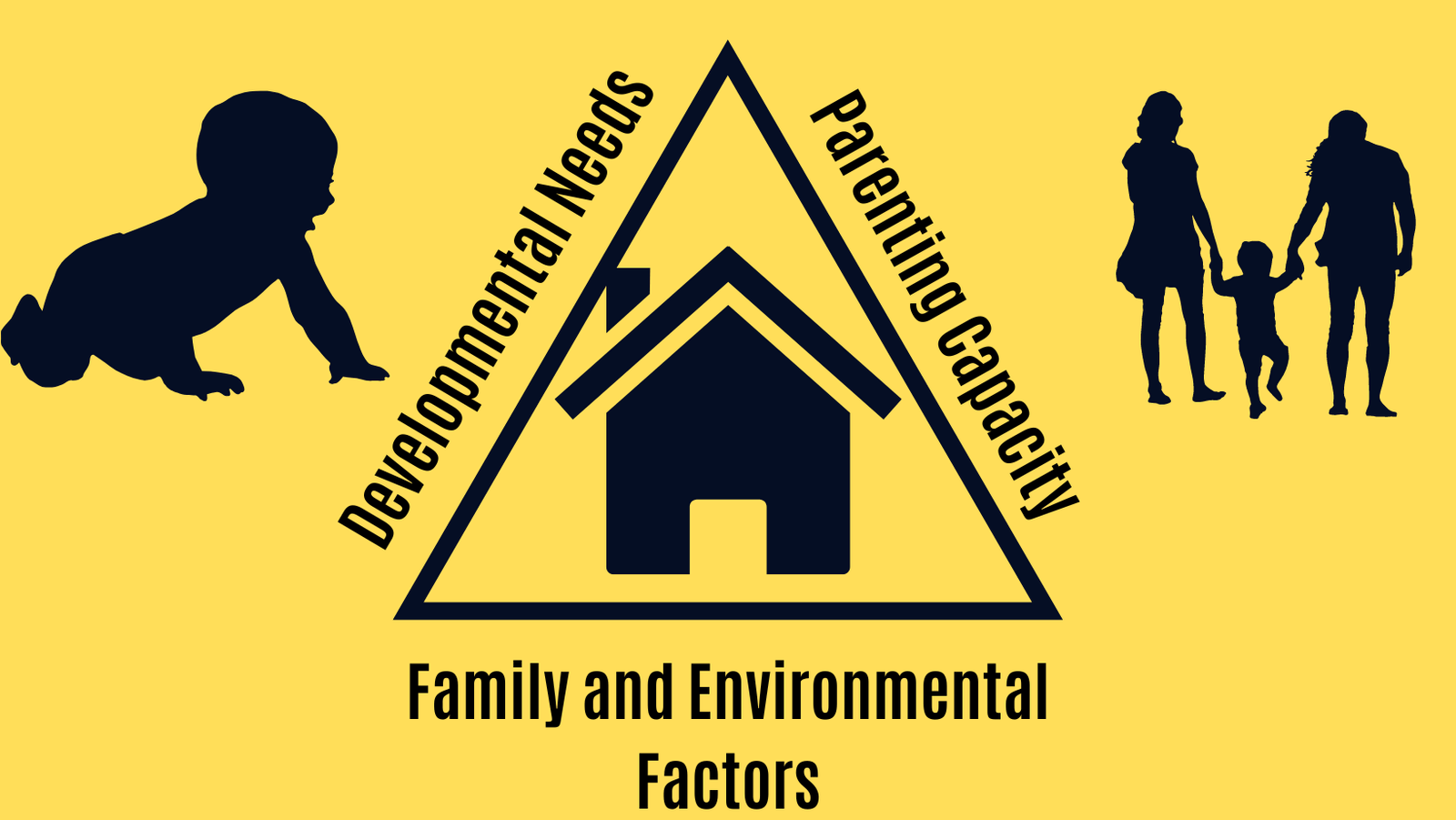
Most social work assessments are based on the Triangle of Needs — a core framework used when evaluating the well-being of children and families. It highlights three interlinked areas that must be considered to support a child’s healthy development: Developmental Needs, Parenting Capacity, and Family and Environmental Factors. Understanding this model helps parents and professionals alike see what the court and CAFCASS are really looking for during assessments.
If you’re being assessed as part of a Section 7 Report or Cafcass safeguarding call, this is one of the core models used to evaluate your parenting, home life, and support network.
Want help preparing for a CAFCASS assessment or social work visit? Message us on WhatsApp for clear, step-by-step guidance.
Developmental Needs
The developmental needs domain is a way of assessing the needs of children in various areas of their development, such as health, education, emotional and behavioural development, family and social relationships, and social presentation and self-care.
Health education addresses the physical and mental well-being of the child, including nutrition, exercise, and disease prevention. Emotional and behavioural development addresses the child’s ability to regulate their emotions and behaviour, and to develop social skills.
Family and social relationships address the child’s interactions with family members and their peers, and their ability to form and maintain healthy relationships. Social presentation and self-care needs address the child’s ability to present themselves appropriately in social situations and to take care of their own physical needs.
The court will often weigh these areas against what’s in the child’s best interest. Learn how that principle shapes decisions in our guide to the child’s best interest in family court.
Unsure how your child’s developmental needs might be judged? Tap WhatsApp and we’ll walk you through what really matters in court.
Parenting Capacity
Parenting capacity refers to a parent’s ability to meet the basic needs of their child, including ensuring safety, providing emotional warmth, stimulating their development, offering guidance and boundaries, and providing stability.
- Basic needs include things like food, shelter, clothing, and medical care. These are the most fundamental needs that must be met in order for a child to survive and thrive.
- Safety needs include things like protection from abuse and neglect, as well as a stable and secure environment. This includes emotional safety, physical safety, and safety from exploitation.
- Developmental needs include things like education, socialisation, and opportunities for growth and self-expression. These needs are important for the child’s overall development and well-being, including emotional, social, and cognitive development.
Ensuring safety involves providing a safe and secure environment for the child, protecting them from physical and emotional harm, and monitoring their well-being. Providing emotional warmth involves showing love and affection, being responsive to the child’s needs, and building a strong emotional bond with the child.
Stimulation involves encouraging the child’s intellectual, emotional, and physical development through activities, play, and learning experiences. Guidance and boundaries involve setting clear rules and expectations for the child’s behaviour and helping them to understand the consequences of their actions.
Stability refers to providing a consistent and predictable environment for the child, including a stable home, consistent routine, and a sense of security. It’s important to note that parenting capacity can be affected by a variety of factors, including a parent’s own emotional well-being, their life experiences and cultural background, and their knowledge of child development.
If you’re facing accusations that could undermine your parenting, it’s essential to understand what evidence the court actually considers when evaluating claims about parenting capacity.
Also, parenting is a continuous learning process that requires the parent to continuously assess and adapt their approach based on the child’s developmental stage, individual needs, and family dynamics.
Facing questions about your parenting capacity? Message us on WhatsApp today and get expert support to present your strongest case.
Family and Environmental Factors
Family and environmental factors are important considerations when assessing a child’s developmental needs. These factors can include family history and functioning, wider family dynamics, housing, employment, income, and family and social integration.
Family history and functioning can include a history of abuse or neglect, mental health issues, substance abuse, and other factors that may have an impact on the child’s development. Wider family dynamics can include the child’s relationships with grandparents, aunts, uncles, and other extended family members, and how these relationships may impact the child’s development.
Housing, employment, and income can also have an impact on a child’s development. For example, living in overcrowded or unsafe housing can have a negative impact on the child’s physical and emotional well-being, while stable employment and a sufficient income can provide a sense of security and stability for the family.
Finally, family and social integration and community resources can also play a role in a child’s development. This includes the child’s relationships with their peers, the availability of extracurricular activities and community resources, and the level of support provided by the community. It’s important to note that family and environmental factors can have both positive and negative impacts on a child’s development, and that addressing any negative factors can help to improve the child’s overall well-being.
Concerns around home life and external risk factors are often explored in fact-finding hearings. These hearings may examine whether allegations about your environment hold any weight in court.
Worried about how your home life will be judged in court? Tap WhatsApp and get tailored advice for your situation.
Final Thoughts
It’s important to note that these areas of development are interrelated and that addressing needs in one area can have a positive impact on other areas. Additionally, it’s important to consider the child’s unique needs and strengths, and to involve the child and their family in the assessment process.
In assessing the needs of children and families, it is important to consider all three areas of the triangle of needs and to develop a plan of action that addresses each of these areas.
🧠 Insider Insight: Lach, our founder, is a qualified social worker who used to write Section 7 reports for CAFCASS — the very reports that influence court outcomes. Now he helps dads respond to them. Learn more about Lach’s background.
👉 Learn more about how we can support you or book a free consultation today
The Triangle of Needs in Social Work
Most social work assessments are based on the Triangle of Needs — a core framework used when evaluating the well-being of children and families. It highlights three interlinked areas that must be considered to support a child’s healthy development: Developmental Needs, Parenting Capacity, and Family and Environmental Factors. Understanding this model helps parents and professionals alike see what the court and CAFCASS are really looking for during assessments.
If you’re being assessed as part of a Section 7 Report or Cafcass safeguarding call, this is one of the core models used to evaluate your parenting, home life, and support network.
Want help preparing for a CAFCASS assessment or social work visit? Message us on WhatsApp for clear, step-by-step guidance.
Developmental Needs
The developmental needs domain is a way of assessing the needs of children in various areas of their development, such as health, education, emotional and behavioural development, family and social relationships, and social presentation and self-care.
Health education addresses the physical and mental well-being of the child, including nutrition, exercise, and disease prevention. Emotional and behavioural development addresses the child’s ability to regulate their emotions and behaviour, and to develop social skills.
Family and social relationships address the child’s interactions with family members and their peers, and their ability to form and maintain healthy relationships. Social presentation and self-care needs address the child’s ability to present themselves appropriately in social situations and to take care of their own physical needs.
The court will often weigh these areas against what’s in the child’s best interest. Learn how that principle shapes decisions in our guide to the child’s best interest in family court.
Unsure how your child’s developmental needs might be judged? Tap WhatsApp and we’ll walk you through what really matters in court.
Parenting Capacity
Parenting capacity refers to a parent’s ability to meet the basic needs of their child, including ensuring safety, providing emotional warmth, stimulating their development, offering guidance and boundaries, and providing stability.
- Basic needs include things like food, shelter, clothing, and medical care. These are the most fundamental needs that must be met in order for a child to survive and thrive.
- Safety needs include things like protection from abuse and neglect, as well as a stable and secure environment. This includes emotional safety, physical safety, and safety from exploitation.
- Developmental needs include things like education, socialisation, and opportunities for growth and self-expression. These needs are important for the child’s overall development and well-being, including emotional, social, and cognitive development.
Ensuring safety involves providing a safe and secure environment for the child, protecting them from physical and emotional harm, and monitoring their well-being. Providing emotional warmth involves showing love and affection, being responsive to the child’s needs, and building a strong emotional bond with the child.
Stimulation involves encouraging the child’s intellectual, emotional, and physical development through activities, play, and learning experiences. Guidance and boundaries involve setting clear rules and expectations for the child’s behaviour and helping them to understand the consequences of their actions.
Stability refers to providing a consistent and predictable environment for the child, including a stable home, consistent routine, and a sense of security. It’s important to note that parenting capacity can be affected by a variety of factors, including a parent’s own emotional well-being, their life experiences and cultural background, and their knowledge of child development.
If you’re facing accusations that could undermine your parenting, it’s essential to understand what evidence the court actually considers when evaluating claims about parenting capacity.
Also, parenting is a continuous learning process that requires the parent to continuously assess and adapt their approach based on the child’s developmental stage, individual needs, and family dynamics.
Facing questions about your parenting capacity? Message us on WhatsApp today and get expert support to present your strongest case.
Family and Environmental Factors
Family and environmental factors are important considerations when assessing a child’s developmental needs. These factors can include family history and functioning, wider family dynamics, housing, employment, income, and family and social integration.
Family history and functioning can include a history of abuse or neglect, mental health issues, substance abuse, and other factors that may have an impact on the child’s development. Wider family dynamics can include the child’s relationships with grandparents, aunts, uncles, and other extended family members, and how these relationships may impact the child’s development.
Housing, employment, and income can also have an impact on a child’s development. For example, living in overcrowded or unsafe housing can have a negative impact on the child’s physical and emotional well-being, while stable employment and a sufficient income can provide a sense of security and stability for the family.
Finally, family and social integration and community resources can also play a role in a child’s development. This includes the child’s relationships with their peers, the availability of extracurricular activities and community resources, and the level of support provided by the community. It’s important to note that family and environmental factors can have both positive and negative impacts on a child’s development, and that addressing any negative factors can help to improve the child’s overall well-being.
Concerns around home life and external risk factors are often explored in fact-finding hearings. These hearings may examine whether allegations about your environment hold any weight in court.
Worried about how your home life will be judged in court? Tap WhatsApp and get tailored advice for your situation.
Final Thoughts
It’s important to note that these areas of development are interrelated and that addressing needs in one area can have a positive impact on other areas. Additionally, it’s important to consider the child’s unique needs and strengths, and to involve the child and their family in the assessment process.
In assessing the needs of children and families, it is important to consider all three areas of the triangle of needs and to develop a plan of action that addresses each of these areas.
🧠 Insider Insight: Lach, our founder, is a qualified social worker who used to write Section 7 reports for CAFCASS — the very reports that influence court outcomes. Now he helps dads respond to them. Learn more about Lach’s background.
👉 Learn more about how we can support you or book a free consultation today